Modules 814 PSychology
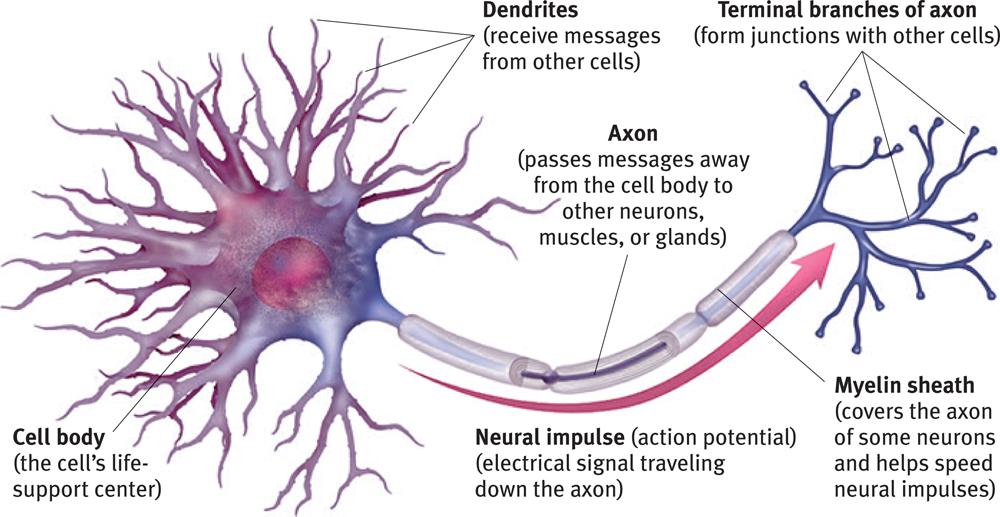
Neuron Anatomy. Nerve Cell: Dendrites receive messages from other neurons. The message then moves through the axon to the other end of the neuron, then to the tips of the axon and then into the space between neurons. From there the message can move to the next neuron. Neurons pass messages to each other using a special type of electrical signal.

Myelinated Motor Neurons Function, Location & Types
Neurons are the basic functional units of the nervous system, and they generate electrical signals called action potentials, which allow them to quickly transmit information over long distances. Glia are also essential to nervous system function, but they work mostly by supporting the neurons.

Nervous system Neurons, Signals, Reflexes Britannica
AboutTranscript. Neurons (or nerve cells) are specialized cells that transmit and receive electrical signals in the body. Neurons are composed of three main parts: dendrites, a cell body, and an axon. Signals are received through the dendrites, travel to the cell body, and continue down the axon until they reach the synapse (the communication.

Motor Neuron The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
Action potential curve and phases (diagram) Hypopolarization is the initial increase of the membrane potential to the value of the threshold potential. The threshold potential opens voltage-gated sodium channels and causes a large influx of sodium ions. This phase is called the depolarization. During depolarization, the inside of the cell.
Parts Of A Motor Neuron
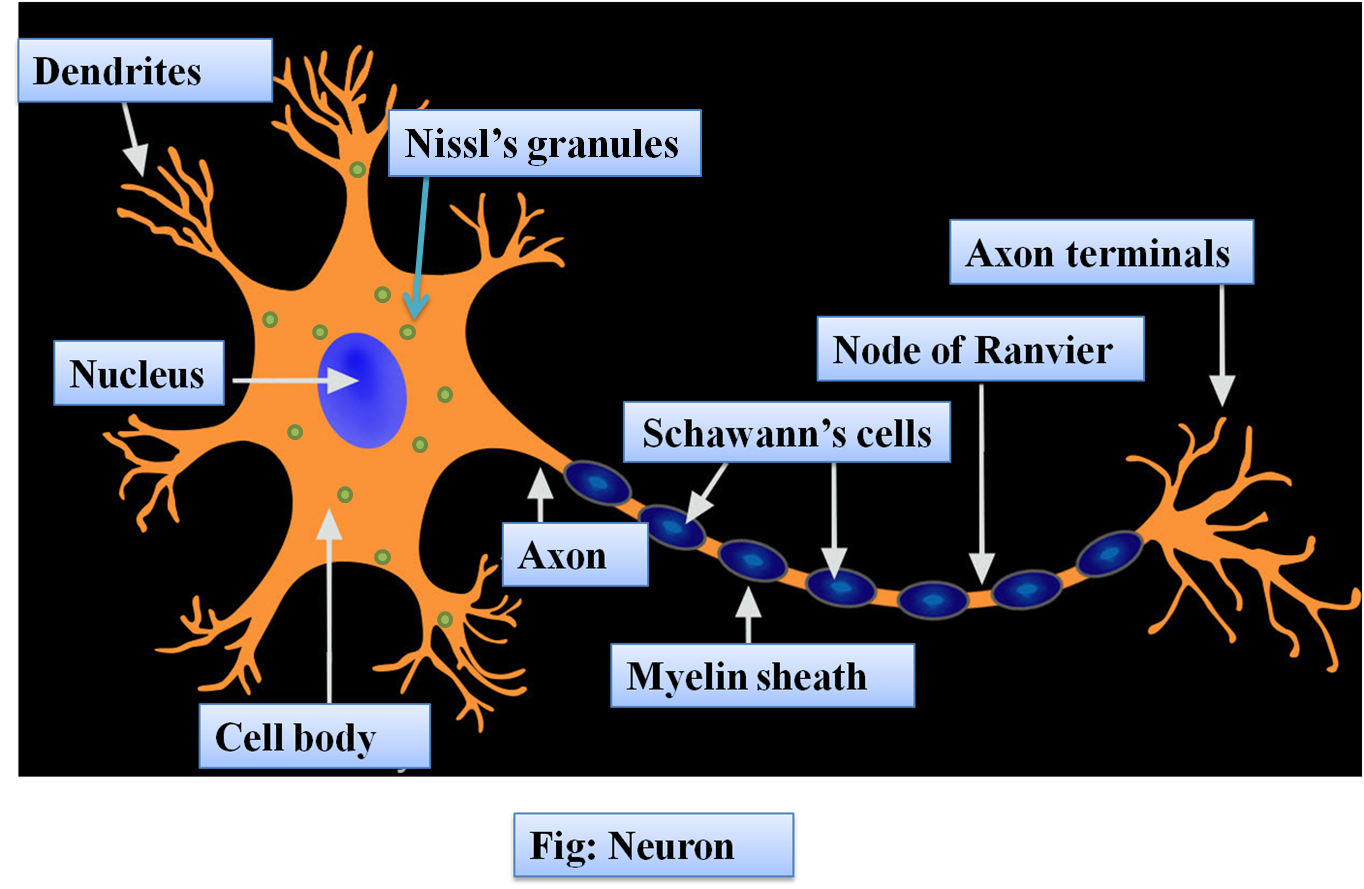
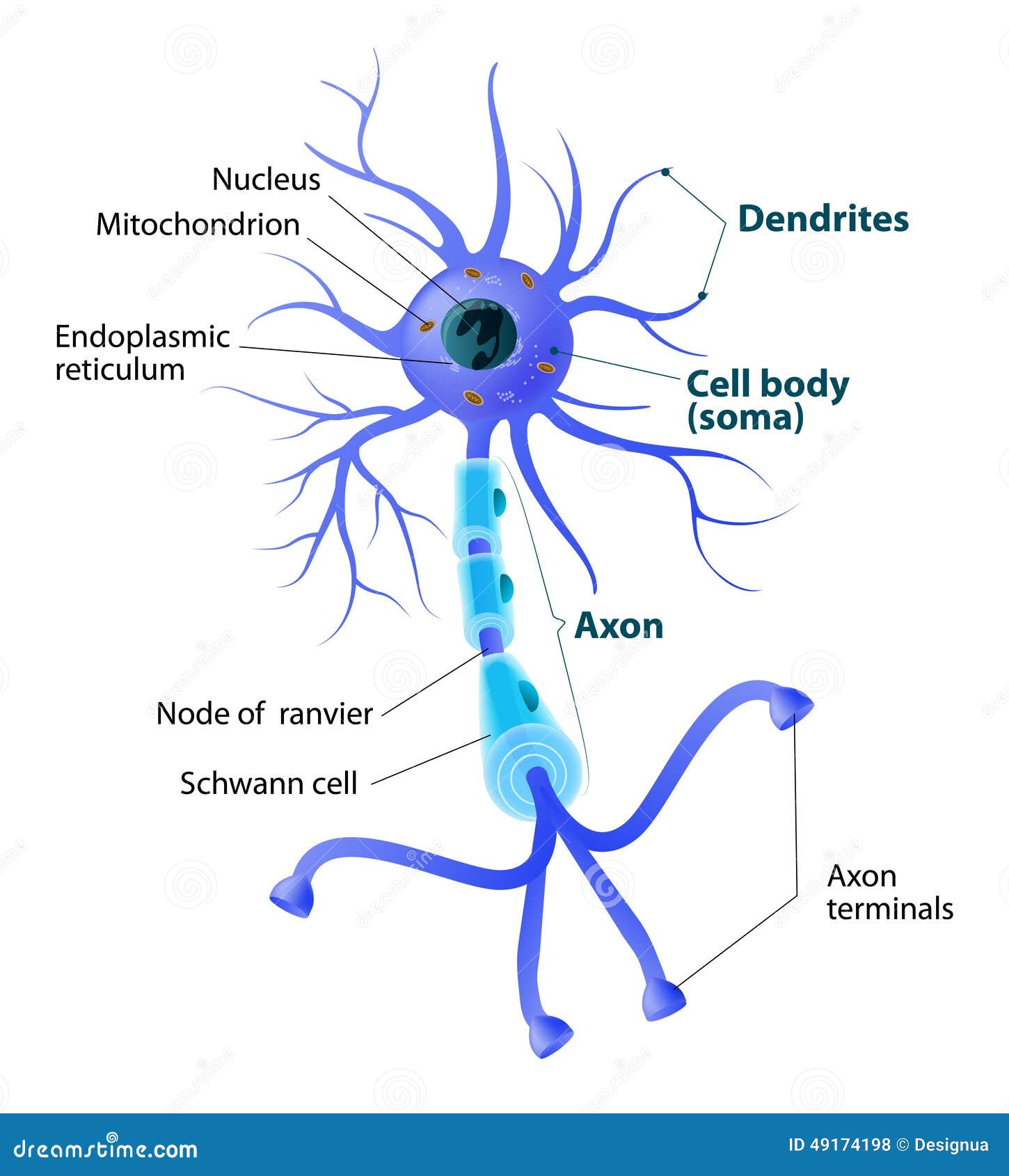
Neuron Structure. Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\) shows the structure of a typical neuron. The main parts of a neuron are labeled in the figure and described below. Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): Somatic Motor Neuron with cell body, axon, axon, myelin sheath, nodes of Ranvier, axon terminal, dendrites, synaptic end of the bulbs, and other associated.
Structure of a Motor Neuron Stock Vector Illustration of care, body 49174198
A motor neuron (or motoneuron or efferent neuron [1]) is a neuron whose cell body is located in the motor cortex, brainstem or the spinal cord, and whose axon (fiber) projects to the spinal cord or outside of the spinal cord to directly or indirectly control effector organs, mainly muscles and glands. [2]

Motor Neuron
Motor neurons (also referred to as efferent neurons) are the nerve cells responsible for carrying signals away from the central nervous system towards muscles to cause movement. They release neurotransmitters to trigger responses leading to muscle movement.

Neuron Diagram Straight from a Scientist
Nervous tissue is composed of two types of cells, neurons and glial cells. Neurons are the primary type of cell that most anyone associates with the nervous system. They are responsible for the computation and communication that the nervous system provides. They are electrically active and release chemical signals to target cells.

The Nervous System (Structure and Function) (Nursing) Part 1
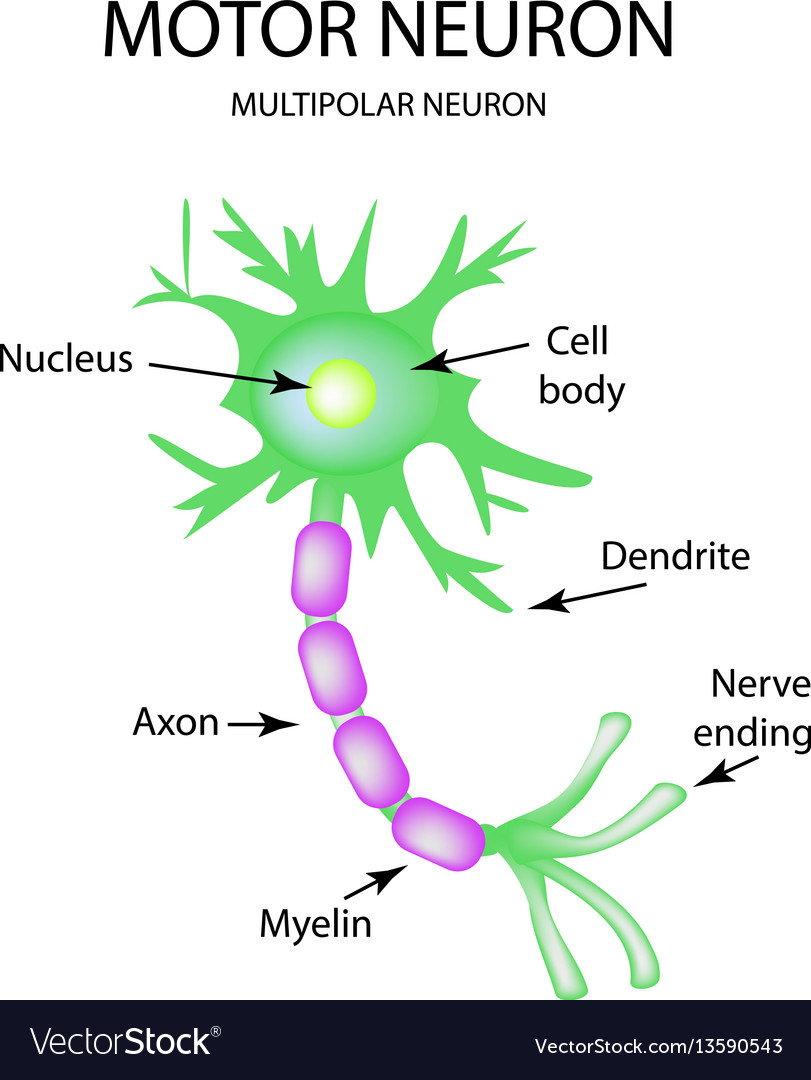
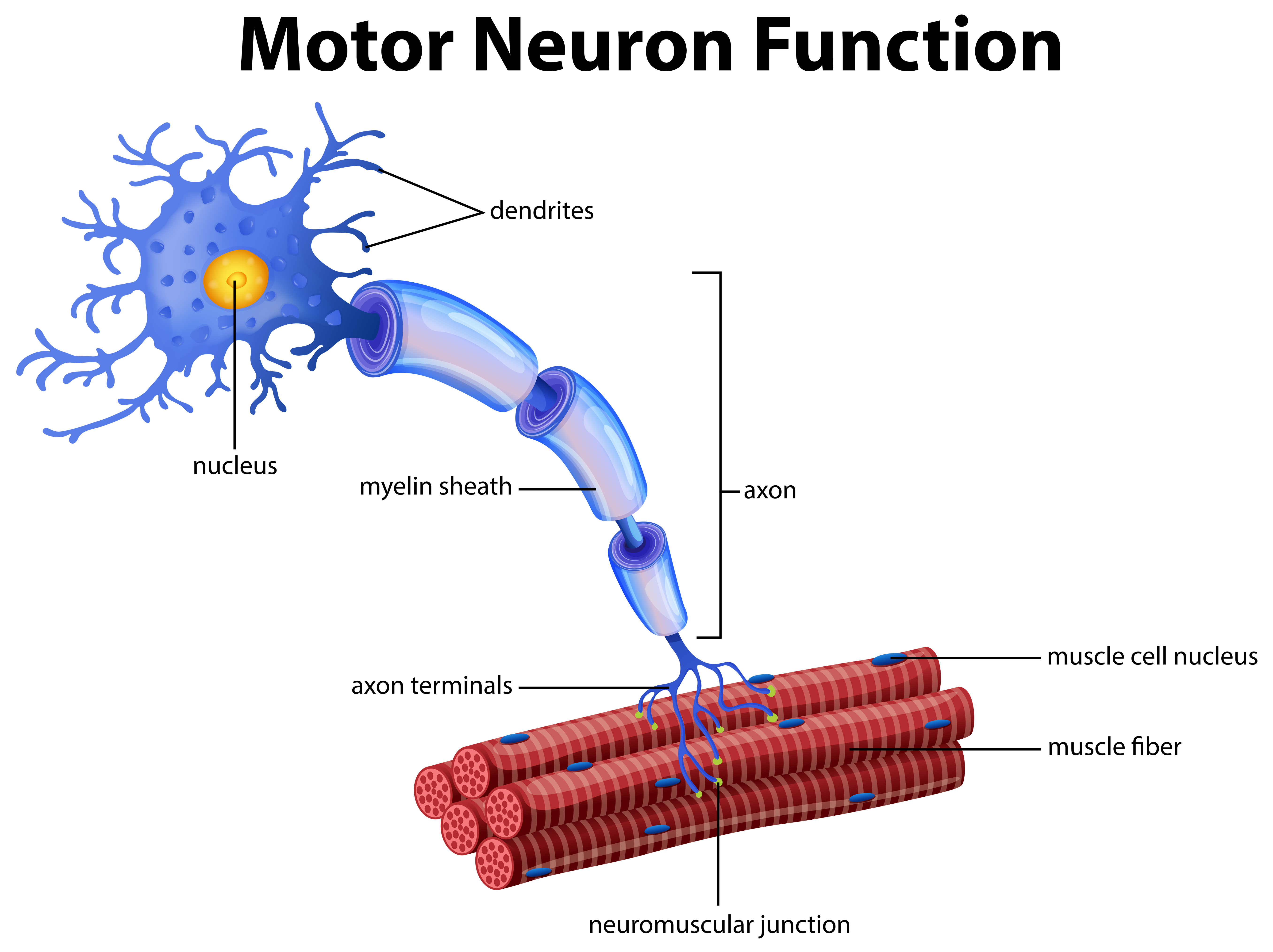
Well-Labelled Diagram of Motor Neuron A motor neuron is a nerve cell that functions to transmit signals from the central area of the nervous system to an effector site such as muscles or glands. A motor neuron can be broadly seen as consisting of three parts - cell body, axon and dendrites.

Figure 7 4 Structure Of A Typical Motor Neuron Bangmuin Image Josh
Definition A motor neuron is a cell of the central nervous system. Motor neurons transmit signals to muscle cells or glands to control their functional output. When these cells are damaged in some way, motor neuron disease can arise. This is characterized by muscle wasting (atrophy) and loss of motor function. Motor Neuron Overview

FileNeuron1.jpg Simple English Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Diagram Of Neuron A neuron is a specialized cell, primarily involved in transmitting information through electrical and chemical signals. They are found in the brain, spinal cord and the peripheral nerves. A neuron is also known as the nerve cell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/neuron-anatomy-58530ffe3df78ce2c34a7350.jpg)
Neuron Anatomy, Nerve Impulses, and Classifications
Let's dive a bit deeper into the functioning of motor neurons as we refer to a neatly labeled diagram. Structure, Function, and Location of Motor Neurons Structure All motor neurons are multipolar neurons. A multipolar neuron has only one axon and densely branched dendrites.

What Is a Neuron? Diagrams, Types, Function, and More
Motor neuron Motoneuron 1/4 Synonyms: Neuron motorium Motor neurons, also known as efferent neurons, are nerve cells responsible for carrying central nervous system signals towards muscles to cause voluntary or involuntary movement through the innervation of effector muscles and glands.

Motor neuron Alila Medical Images
Sherrington was the first to recognize this fundamental relationship between an α motor neuron and the muscle fibers it innervates, for which he coined the term motor unit. The motor unit. (A) Diagram showing a lower motor neuron in the spinal cord and the course of its axon to the muscle. (B) Each motor neuron synapses with multiple muscle.
The structure of the motor neuron infographics on Vector Image
An Easy Guide to Neuron Anatomy with Diagrams By Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc Updated on November 9, 2023 Reviewed by Saul Mcleod, PhD Neurons are the information processing units of the brain responsible for sending, receiving, and transmitting electrochemical signals throughout the body.
A Vector of Motor Neuron Function 296405 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Motor neurones are cells in the brain and spinal cord that allow us to move, speak, swallow and breathe by sending commands from the brain to the muscles that carry out these functions. Their nerve fibers are the longest in the body, a single axon can stretch from the base of the spinal cord all the way to the toes. Motor neurons divided into either upper or lower motor neurones, forming.